
Investing capital always involves some level of risk. These risks are heightened when all funds are put into a single asset rather than diversifying across multiple ones.
Yet, this form of investment still exists. We will talk about when it is used, what factors need to be considered, and its benefits and drawbacks in this article.
More information about other investment methods, their types, and the characteristics of different forms of investment can be found in the article "Investments for beginners."
Understanding direct investments
Direct investments are characterized by the investment of capital in a single asset. People thinking about investing money in assets often hear the advice not to "put all their eggs in one basket." This means it's unwise to invest all funds in a single asset; it's better to spread the investment amount across several instruments.
However, direct investments represent a complete contradiction to this advice. Their key feature is precisely investing capital in a single asset.
This often involves investing in a specific company – buying a large block of shares or a stake in the business, facilities, or equipment. This gives the investor the opportunity to have control over the company and participate in its management.
They do not always manage directly. They may appoint their representative to the board of directors and exercise control and other functions through them.
Given all this, direct investments involve large sums of money. Therefore, companies, and less frequently individuals, usually act as investors.
These investments are long-term and among the least liquid. Capital is invested for a long period since time is needed to start and fine-tune business processes, i.e., for the full-fledged functioning of the company.
Such investments are less liquid because it takes time to recoup the invested funds. However, the investor can earn income from the activities of the investment target company.
Types of direct investments
Since there are several ways to invest capital that involve the possibility of controlling and managing the investment object, several main types of direct investments are distinguished:
1. Vertical investments refer to capital investments aimed at deepening the current processes of a company. For instance, this could be an automobile manufacturing company acquiring a business that produces automotive glass.
In other words, it is about purchasing companies that can perform some functions or processes that the enterprise would otherwise have to outsource and pay for each time.
2. Horizontal investments aim to increase influence and spread, including geographically. This involves opening new stores, and sales points, including through franchises, and expanding into foreign markets.
3. Conglomerate investments imply the merger of several companies, which are not related to one area or field of activity, into one large enterprise. Thus, groups of companies engaged in different activities under a single management are formed.
Based on territorial characteristics, direct investments can be:
- Domestic, i.e., made by an investor in the country of which they are a citizen;
- Foreign, i.e., investments in foreign countries. Here, two subtypes are distinguished:
- Outward: carried out by citizens and legal entities of a certain country abroad;
- Inward: investments coming into a country from other states.
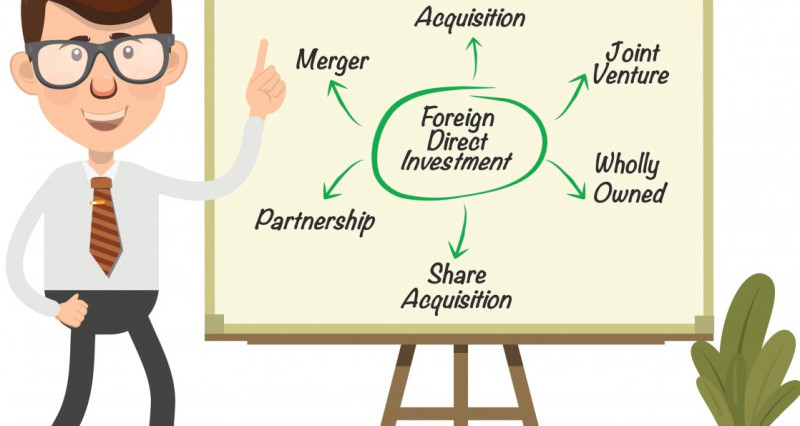
Depending on the form, investments are made in the form of:
- Mergers: the voluntary union of two or more enterprises;
- Acquisitions: the merger of a larger enterprise with smaller ones in the same industry by acquiring a large stake in their business;
- Establishing a subsidiary: unlike the previous types, this involves creating a separate legal entity controlled by the parent company.
How to earn on direct investments
Direct investments are not just about investing capital for the purpose of saving or increasing one’s savings. They offer the opportunity to directly influence the development of business and the economy as a whole.
This contributes to the creation of new jobs, the production of goods, or the provision of services needed by the population. Thus, this investment is not just in any specific enterprise, but in the economic growth of the entire state.
In this case, the investor contributes not only their finances but also their abilities, talents, and competencies – everything that can enable a company to grow and develop.
Such investors are called "smart" investors. They use their own developments, connections, experience, and capital to grow businesses.
Subsequently, they earn profits from the growth of these companies. This is particularly true for young, developing companies that lack funding to enter the "big" arena. However, there is undoubtedly a high risk that the startup may never achieve real success in business.
Another way to earn money is not just by financing a company but also by taking on a leadership position in it. This allows not only direct participation in business management but also a steady income.
Additionally, there are options for earning passive income. For example, stable payments such as dividends, which companies pay monthly or quarterly to their shareholders, are a form of passive income.
The sale of shares itself is also a way to make money. However, it is important to understand that when it comes to large blocks of shares, such transactions can lead to a sharp collapse in the stock prices not only of the specific company but also of the entire industry in which it operates.
How much you can earn
We have already talked a lot about what direct investments are and how to earn from them. However, an equally interesting question is what kind of income one can derive from them.
Here, it is important to differentiate between public and private companies. Calculating income from private enterprises, that do not disclose their financial statements, is quite challenging. However, according to analysts' estimates, the income from direct investments in private companies averages 15-17% annually.
As for public companies, those whose securities offers are listed on stock exchanges, calculating potential income is considerably easier. This is because all information about stock prices, dividends, and financial statements is publicly available.
Investing capital in public companies primarily involves buying their stocks. Consequently, there are two ways to earn income: through company dividends on shares or through an increase in the value of the securities themselves.
In some cases, both of the above methods can be combined. However, not all companies pay dividends to their shareholders, and this can be due to various reasons. For example, many developing companies prefer to reinvest profits back into their business rather than distribute them among shareholders.
At the same time, most large companies pay dividends, and their stock prices tend to increase over time. However, such growth in stock value is relatively moderate, as these companies are already at the peak of their development. Therefore, growth in such assets can average 7-10%.
If we consider promising companies that are going public for the first time, the growth of their stocks can be a hundred- or even thousand-fold. This means that even by investing a relatively small amount of money, one can earn a 100% or even 1000% return.
Nevertheless, it is important to understand that the higher the potential return, the higher the possible risk. This rule applies to all investments, and direct investments are no exception.
Therefore, before investing capital in any enterprise, it is necessary to conduct a thorough analysis of its current state and assess its real development prospects.
Foreign direct investments
One of the most common types of direct investments is international investment. This kind of investment contributes to the economic growth of countries through the attraction of foreign capital.
This becomes particularly relevant for developing countries. For example, a few decades ago, European and American companies began actively transferring their production to China, building their factories there, which continue to operate to this day.
These investments have allowed China to become one of the world leaders, significantly increasing its GDP and the standard of living in the country. Now, China itself acts as an investor, investing funds in other countries.
States are interested in receiving foreign investments, as this contributes to their development and access to innovative technologies. However, the attractiveness of a particular country to foreign investors is also an important factor.
This includes the overall economic climate in the country, openness to innovation, the possibility of receiving benefits or other preferences that can attract investors from abroad.
Investors are often large enterprises from developed countries, investing in existing productions or building new factories, opening branches of their companies, and so on.
However, the positive effects of foreign direct investments are not limited to states as a whole. The end consumer also benefits: by optimizing and reducing expenses, companies manage to lower the cost of production.
Nevertheless, for local producers, the arrival of large foreign enterprises can create some problems, such as increased competition, a shortage of labor, rising service costs, and so on.
Pros and cons
Like any other type of investment, direct investments have both positive and negative aspects. Let's consider the advantages and disadvantages of this type of investing.
The advantages of direct investments include:
- The right to manage the company. By acquiring a large block of shares, the investor gains the ability to influence the future development of the company. The larger the investor's stake, the greater the influence they can exert;
- Additional income. In addition to counting on the growth of the company itself, the investor can claim a portion of the profits generated by the enterprise’s operations;
- High potential profitability. Investing capital in the "right" company at the stage of its inception, when its shares are not worth much but have growth potential, can yield significant profits. This requires selecting promising industries and companies;
- Increasing the GDP of the state. This applies more to foreign investments, which allow bringing currency into the country. This leads to an increase in the country’s GDP and, along with it, the well-being of its citizens. Additionally, it creates healthy competition and new jobs.
The disadvantages of this type of investment are:
- Low liquidity. Such investments are among the least liquid. Money is invested for a long period without any possibility of using it for other purposes. Getting rid of part of the assets in the portfolio is relatively easy, but here there is only one asset;
- Large capital investments. Direct investments require large sums of money. Therefore, for many private investors, this becomes a barrier, and such investing is undertaken by large companies and organizations;
- High risk. The enterprise in which the investor invests capital may ultimately not succeed or go bankrupt. In such a case, the investor not only fails to make any profit but also incurs losses.
Direct and portfolio investments
Investing resources into various instruments can serve different purposes. As mentioned earlier, direct investments aim to gain business management opportunities and direct participation in its activities.
However, this is not necessary for all investors. Many of them simply want to preserve or increase their savings. For such purposes, creating investment portfolios, which include several instruments, is more suitable.
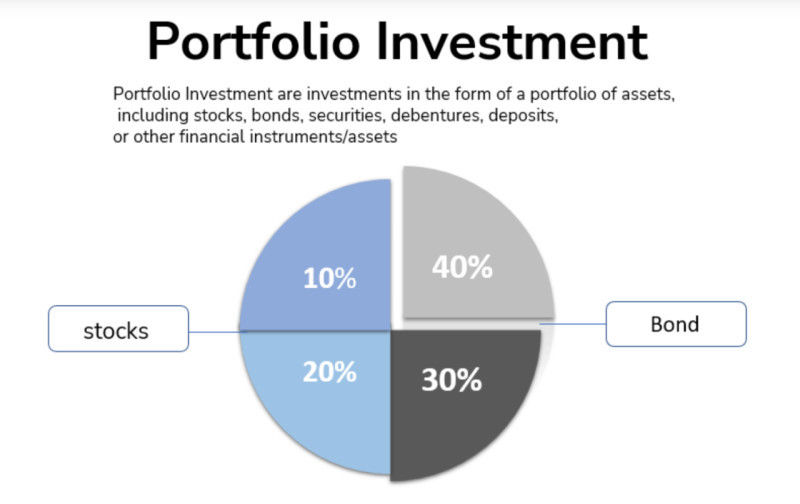
Investors can create portfolios independently or with the help of professional consultants who can assist in selecting the optimal combination of assets.
In this way, the entire capital intended for investment is divided into parts, which can be equal or different. Such division helps investors to reduce potential risks as if one of the assets decreases in value, others can compensate for these losses.
Let's explain it with a specific example: if an investor has $10,000 and pours this entire amount into stocks of a particular company, and after some time these stocks drop in price by 50%, they immediately lose $5,000.
Now, imagine the same $10,000 is distributed equally among several assets: stocks, bonds, gold, real estate, and a bank deposit. If the stocks fall by 50% in price, the investor loses only $1,000, or these losses can even be offset by other assets.
Portfolio investments allow investors to be more flexible and achieve their goals within set timeframes. Depending on the investment horizon and the amount of initial capital, the appropriate combination of instruments is selected.
Funds are often not invested in equal shares. Depending on the risk profile, a portfolio may have a larger share of more aggressive or more conservative assets.
The amount of initial capital for portfolio investments can be significantly lower than for direct investments. Besides, investment portfolios are more liquid and flexible, as they can be rebalanced over time by removing some assets and adding others.
What is investment fund
If an investor lacks personal finances to make direct investments, there are other options for investing funds. One such opportunity, besides the portfolio investments mentioned earlier, is participating in investment funds.
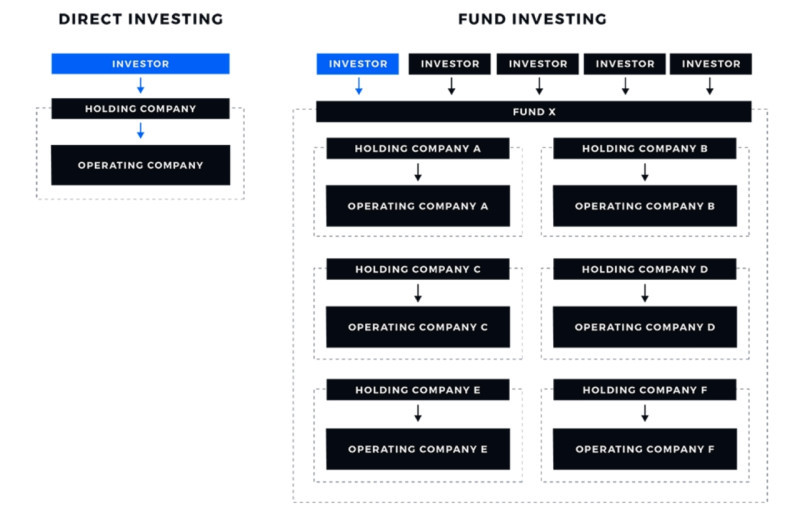
Mutual funds pool resources from several investors and invest them in one or more instruments to generate profit. The resulting income is then distributed among all the fund's participants.
Each of these organizations has a manager or a company that conducts all operations, manages the fund's resources, and bears responsibility for them. A fund is not a business; it's a coalition of capital from several people and assets purchased with these funds.
Moreover, funds can also have their securities: shares, units, or stocks. An investor who puts money into a fund becomes the owner of a portion of all the property, but not of any specific asset.
Funds earn income in two ways: from the increase in the value of the assets themselves or from receiving payments such as interest or dividends. All the income earned is distributed proportionally to the investors' shares in the fund.
The attractiveness of this investment method lies in the fact that the investor does not need to conduct an analysis or decide which assets to invest in independently. All these decisions are made by the manager. The returns from mutual funds can reach up to 20% annually, which is a very good indicator.
Such funds are a form of trust management. Essentially, the investor hands over their resources to other people or a company to manage and can later claim a portion of the income.
Venture capital fund
One type of investment fund directly related to making direct investments is a venture capital fund. Like any other mutual funds, these funds receive money by pooling capital from several investors.
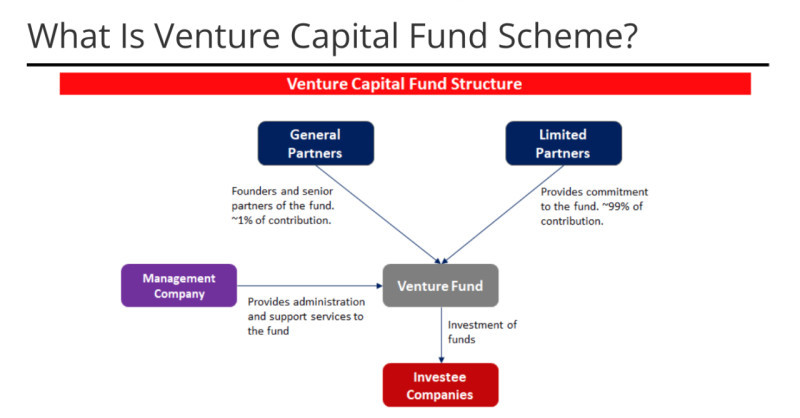
A key difference from other funds is where venture capital funds invest. These funds invest capital exclusively in young, developing companies, hoping for their future growth.
This type of fund is among the highest-risk because, according to statistics, more than 70% of startups "burn out" and become unprofitable, while only about 20-30% can continue operating and generate profit.
However, the income from even 20-30% of promising companies can more than compensate for losses from other, less successful ventures. Therefore, choosing specific assets, or more precisely, companies to invest in is critical for the fund.
Regarding the returns of such investments, as mentioned, some projects can yield as much as 1,000%. However, such projects are rare, so the overall return on venture capital funds is about 27-30% annually. This significantly exceeds the potential income from many other instruments, but the risks are also much higher.
One subtype of venture capital funds is the so-called seed funds. They invest in projects at the idea formation stage or the main concept of the future enterprise, not in already established companies.
Venture funds work with a company until it reaches a certain predetermined profitability level. As a general rule, the return to capital ratio should be 4-8%.
After the company reaches this mark, the fund exits the organization and distributes the money among its participants or invests it in another project.
Conclusion
In this article, we have examined the features of direct investments as a form of resource allocation. It allows you to control and direct management of the company or project in which funds are invested. This is achieved by acquiring a controlling stake or a large share in the company. Direct investments influence not only the growth and development of a specific company but also the economy as a whole.
Direct foreign investments, in particular, significantly impact economic growth. They attract additional capital to the country, build new enterprises, create jobs, and foster healthy competition.
However, it is important to understand that investing in companies, especially young ones, is costly and risky. Many startups ultimately do not achieve their goals and simply go bankrupt.
Often, direct investments are undertaken by large enterprises, as private investors lack the resources for this. However, they can pool their capital and form special funds that invest in a specific company or project.
You may like:








 Back to articles
Back to articles

