ATOM cryptocurrency is the native token of the Cosmos Hub blockchain. This cryptocurrency is used for transaction fees and to enhance network security against cyber-attacks.
ATOM is an inflationary cryptocurrency, with the total coin issuance increasing annually by 7% to 20%.
The Cosmos blockchain represents a secure and scalable blockchain ecosystem, where no less than a thousand decentralized applications from the US interact with each other. Thus, Cosmos is an entire system of blockchains that can scale and interact with each other.
Today, the Cosmos ecosystem boasts a highly active community of developers, users, and investors. The project has dedicated many popular social groups, accounts on the X social media platform, blogs, and various resources.
The most popular niche resource is the Cosmos Forum, where programmers and users actively discuss the network and its many applications. While the number of users is not very large, their engagement is high.
For example, the Cosmos account on the X platform has over 500,000 followers. The Cosmos Blog is equally popular, constantly posting the latest news and announcements aboitself ut upcoming network updates.
In this article, we will delve into the history of the Cosmos project, its main characteristics, and how it distinguishes itself from other similar projects. We'll examine the native blockchain token ATOM, its tokenomics, and touch upon the prospects for the development of both the project itself and its cryptocurrency.
History of Cosmos project

The Cosmos project is today universally acknowledged as one of the most famous and promising in the crypto world. As of preparing this material, it ranks in the top 20 largest projects by market capitalization, according to Coinmarketcap, the world's most popular website for tracking cryptocurrency prices.
Cosmos stands out as one of the few projects that have offered the crypto community an open and flexible infrastructure for blockchain applications. This infrastructure is based on blockchain technology, enabling the creation of new blockchain networks and facilitating interactions among them. Cosmos infrastructure can easily integrate with other ecosystems, providing the ability to create decentralized applications using various blockchain networks, thereby addressing scalability issues and significantly reducing network load.
The Cosmos project was founded in 2014 by a team of developers led by Jae Kwon, an American programmer and entrepreneur who was working on the Tendermint consensus algorithm. Kwon aimed to develop a protocol that could support a wide range of applications and use cases, from payment systems to gaming platforms.
In 2005, Jae Kwon graduated from Cornell University with a bachelor's degree in computer science. He then worked in Silicon Valley at companies like Alexa and Yelp. Before Cosmos, Kwon founded the service iDoneThis and collaborated with open-source projects such as CoffeeScript and Scramble.io. His involvement in these projects fueled his desire to create the Tendermint protocol.
Around 2013, Kwon conceptualized the idea of developing a blockchain based on a Proof-of-Stake system. At the time, developers were unsure how to implement such a task. So, Kwon reckoned that the idea was premature, and he continued to work in the cryptocurrency exchange industry.
During those years, Kwon studied various scientific publications from the late 1980s. Among these materials, he discovered a paper titled "Consensus in the Presence of Partial Synchrony," authored by Massachusetts Institute of Technology professors Cynthia Dwork and Nancy Lynch. This paper detailed the results of classic BFT research and the components necessary for creating a PoS system.
Inspired by this research, Kwon decided to develop a BFT protocol based on Proof-of-Stake that could scale to hundreds of nodes in a decentralized environment, leading to the conception of the Tendermint protocol. This was the first Proof-of-Stake consensus algorithm developed using the Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) protocol.
Kwon was concerned about Bitcoin's high energy consumption as a global currency, which motivated his team to launch Tendermint in search of a more environmentally friendly cryptocurrency.
In 2014, Kwon founded the software development company Tendermint Inc in California and published the project's whitepaper. In 2015, developer Ethan Buchman, who previously worked at Eris Industries (later renamed Monax), joined Kwon. Their collaboration led to the creation of the non-profit organization Interchain Foundation (ICF) where they served as president and vice president, respectively.
In 2016, Kwon officially founded Tendermint Inc., focusing on his ambitious new project: the Cosmos ecosystem. The developers envisioned a project that would seamlessly combine other blockchains, an idea that was almost deemed unachievable in the crypto community at the time.
During the development process, programmers at Tendermint believed that scaling the network was only possible by interconnecting numerous blockchains. However, this required inventing infrastructure that would allow these blockchains to interact with each other, exchanging information. Furthermore, blockchains based on this infrastructure needed to manage their tokens and assets.
The core of the Cosmos project was an algorithmic structure enabling the creation and management of blockchains based on Proof-of-Stake. This operating principle was intended to significantly improve network performance and ensure faster transaction processing.
In the summer of 2016, Tendermint held its first funding stage. In 2017, the Interchain Foundation, which promoted decentralized applications on the Cosmos network, contracted with All in Bits Inc to develop the Cosmos Network project. The company's first token IPO in 2018 raised a staggering $9 million. During this event, the company sold 75% of the total token issuance of ATOM, with 5% reserved for seed investors, and All in Bits Inc and the Interchain Foundation each receiving 10%. That same year, in its second funding round, the company raised an additional $17 million in ETH, BTC, and US dollars.
In that year, Cosmos joined the Ethereum Community Fund, an initiative to create a special fund to encourage blockchain infrastructure development. Kwon's team launched Ethermint on Tendermint and Basecoin, a framework for creating digital currencies that use the Go programming language (Golang) and support plugins with various additional features. This allowed the Tendermint team to announce the launch of Cosmos Hub in 2019 – the first in a series of Proof-of-Stake blockchains.
In March of the same year, 100% of the native tokens (ATOM cryptocurrency) were distributed to early investors, the ICF fund, and developers from the genesis block. Trading of the native token on exchanges began in April.
By 2021, there were already over 250 projects within the Cosmos ecosystem. Many large companies did not hesitate to invest in Jae Kwon's idea, including significant organizations such as the American hedge fund Pantera Capital, Canada's largest producer of acoustic systems Paradigm, cryptocurrency venture fund 1confirmation, American investment company Polychain Capital, and many others. Moreover, the Cosmos project caught the interest of well-known personalities in the crypto world, such as blockchain technology enthusiast and Ethereum co-founder Joseph Lubin, creator of the peer-to-peer electronic payment system and Litecoin founder Charlie Lee, investor and founder of Digital Currency Group Barry Silbert.
It's clear that the project's scalability, which intrigued many investors, was its main feature. They understood that this project could solve the scalability issue of blockchain technologies, thereby allowing the crypto community to develop more complex applications and networks.
Today, the Cosmos project is recognized as one of the most scalable in the crypto world. It offers blockchain developers exceptional opportunities, from creating decentralized applications to implementing cross-chain solutions.
What lies behind uniqueness of Cosmos project

To understand the uniqueness of the Cosmos project, it's essential to recognize why it is widely acknowledged as a blockchain 3.0 in the crypto community.
Let's start in order. Blockchain 1.0 is the first cryptocurrency, Bitcoin, which kickstarted the entire industry and remains the largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization nowadays. However, Bitcoin's blockchain function is limited to recording transactions.
Today, Bitcoin has a vast ecosystem and is widely used for transferring value, rightfully earning the title of "digital gold," despite its slow transaction processing times and lack of additional functionalities.
When referring to blockchain 2.0, Ethereum emerges as the primary candidate. Beyond being a decentralized network, Ethereum introduced Solidity, a programming language designed for developing applications and smart contracts that operate within its blockchain.
Ethereum's functionality vastly exceeds Bitcoin's, but smart contract development is constrained by the network's strict rules, limiting developers' ability to modify them according to their needs.
Ethereum, like other 2.0 blockchain projects, faces three main challenges:
- Scalability. Network growth leads to slow and costly transactions, particularly noticeable in the decentralized finance (DeFi) sector, rendering ETH impractical for DeFi projects.
- Sovereignty. Developing applications on Ethereum's platform severely limits the ability to expand beyond its functionality.
- Usability. Ethereum's functionality restricts developers from creating complex products and applications.
Ethereum 2.0 might address scalability to some extent, and Layer 2 projects like Optimism could partly solve the sovereignty issue. However, usability and limited functionality remain unresolved.
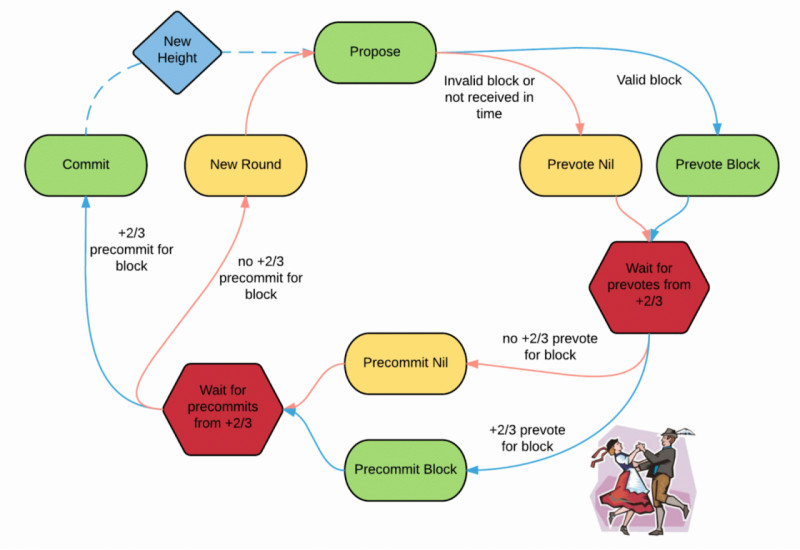
Now, let's examine how the Cosmos project is structured. Cosmos operates on the Tendermint Core protocol, utilizing the Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) consensus algorithm.
A consensus algorithm ensures nodes in a distributed system agree on the state of the network. Only those resistant to Byzantine failures are viable in public blockchain systems, including:
- Classical consensus protocols (e.g., PBFT)
- Nakamoto Consensus (e.g., Proof-of-Work)
Tendermint protocol is based on classical BFT consensus, ensuring 100% transaction finality and deterministic block production, along with a presumption of synchrony in the network's state.
Cosmos is an ecosystem that allows the integration of diverse blockchains. It enables the creation of decentralized applications or the launch of new blockchains quickly and cost-effectively.
The essence of the Cosmos project is as follows: when creating decentralized applications and blockchains, there's a unique opportunity to connect with other blockchains within the same ecosystem and with external blockchains, all thanks to what are called decentralized bridges.
The Cosmos ecosystem can confidently be labeled as blockchain 3.0 because it has the capability to address issues related to scalability and those that arise from limiting developers to a single network.
Tools like Tendermint and the Cosmos SDK enable developers to quickly create secure, interoperable, and most importantly, scalable blockchain applications. These tools allow for open interaction both within and outside the network.
For example, a blockchain built on the Tendermint base can merge with the Ethereum blockchain, which is unrelated to the Cosmos network.
Tendermint, combined with the Application Block Chain Interface (ABCI), allows developers to create applications in various programming languages.
Thus, by designing a blockchain on the Tendermint core, developers can focus on their product without worrying about consensus or security issues and create applications in any language of their choice.
Creating a product based on Cosmos grants developers the right to choose validators for their blockchain. This facilitates the realization of highly decentralized public networks with a large number of validators, as well as the creation of private networks with specific validators.
For instance, the Binance Smart Chain network is private, yet only validators selected by Binance's administration are authorized to confirm transactions in this network.
The uniqueness of the Cosmos network also lies in its ability to allow different blockchains to interact within a single ecosystem. For example, users may need to transfer coins from one blockchain to another, but the coins are not actually transferred; they are locked in blockchain A and created in blockchain B. Subsequently, the coins in blockchain B begin to "live," while the coins in blockchain A remain "frozen" and cannot be used until they are returned from blockchain B.
This scheme closely resembles a smart contract in the Ethereum network but operates between different blockchains. All interconnected blockchains form a network where the Cosmos Hub acts as the connecting hub.

The Cosmos Hub is the first blockchain launched within the Cosmos Network ecosystem and is also the central element of this ecosystem. The main task of the Cosmos Hub is to keep track of the total number of digital coins in each zone (i.e., blockchain) of the ecosystem, allowing zones to directly transfer digital coins to each other.
The Cosmos Hub uses the Tendermint consensus algorithm, through which validators stake (i.e., lock) ATOM tokens.
The ATOM cryptocurrency is the native asset of the Cosmos Hub, divisible into 1 million micro-ATOMs (uATOM). ATOM functions as a so-called work token. For instance, users can stake tokens themselves or delegate them to a validator, thereby increasing his rating and earning a portion of the profit.
Depending on the number of staked tokens, a validator has a proportional share of the vote, enabling them to form blocks and receive rewards in the form of new ATOM tokens. Annually, between 7% to 20% of tokens are issued from the total emission.
Validators distribute a portion of the block reward to delegating users, considering the network tax retention. Like PoW networks, validators charge a commission for combining "voting shares." Validators must honestly confirm blocks, participate in system governance, and operate a high-performance hardware server. The operation of such a server, by the way, costs from $10,000, a price that is expected to increase as the blockchain grows.
A validator failing to meet these responsibilities is stripped of tokens and the corresponding status. The architecture of a validator can change, directly affecting the network's security level. Generally, the higher the security level of the architecture, the higher its cost, including maintenance costs.
To enter the active set, a validator only needs to surpass a certain threshold level. The validator in the 125th place has slightly less than $250,000 delegated to them. Thus, if a validator lacks this amount or no one delegates it to them, they cannot enter the active set.
In the first year after the mainnet launch, only 125 validator slots are available. Over the next 10 years, this number is expected to increase to 300. The network's inflation rate is set at a minimum of 7% to 20%.
The block reward is adjusted based on the declared target participation level in staking. All coins must be staked for 21 days, with owners unable to immediately sell them after staking. The network tax is directed to a reserve pool, which funds are used to enhance the security of the Cosmos Network.
Specifics of ATOM cryptocurrency

The ATOM cryptocurrency, as the native token of the Cosmos ecosystem, is used for network protection, incentivizing validators, and paying for transactions.
Validators, in turn, are responsible for maintaining the network. For their work, they earn profits in the form of ATOM tokens. Users have the opportunity to stake their ATOM tokens to receive rewards. Additionally, the ATOM cryptocurrency can be used as a token holder's vote, giving the user a say in decisions related to the governance of the Cosmos platform.
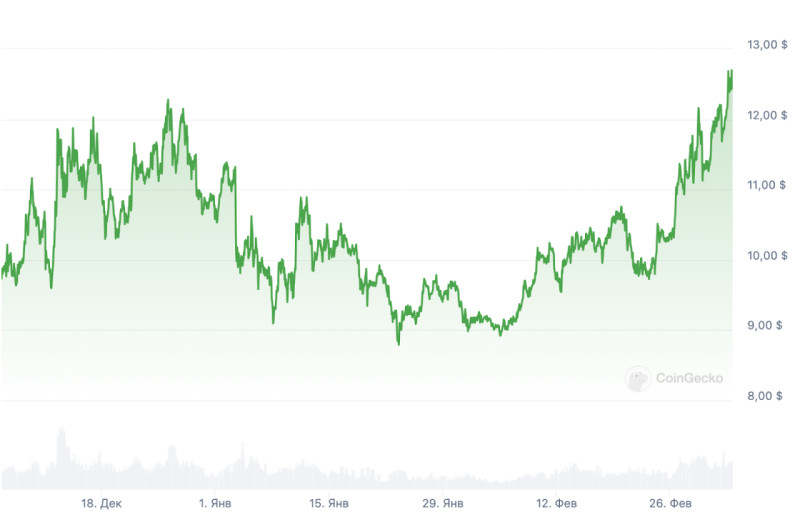
The issuance of ATOM coins is limited to a total of 286 million tokens. Of these, approximately 190 million were issued at the project's launch, indicating that the remaining coins are released gradually over the following years. The price of ATOM at the time of writing this material is $12.45 (ATOM/USD trading pair).
ATOM cryptocurrency cannot be mined. Network users earn it through staking, as the network uses a PoS algorithm. The protocol limits the annual issuance of the cryptocurrency to within 10% of the circulating supply.
ATOM cryptocurrency is traded on all major centralized cryptocurrency exchanges:
- Coinbase
- Binance
- KuCoin
- WhiteBIT
- Kraken
The market capitalization of the ATOM token is $4,851,218,612. According to this indicator, the cryptocurrency ranks 26th in the ranking of the largest cryptocurrency data aggregator CoinGecko. The market capitalization is calculated by multiplying the price of the tokens by their quantity in circulation. Currently, there are 388.97 million ATOM tokens in circulation.
Prospects of Cosmos (ATOM) token
Currently, the ATOM token of the Cosmos blockchain is traded on the largest cryptocurrency exchanges. The Cosmos project, which has no analogues in the crypto market, is one of the most popular and ranks in the TOP-50 by market capitalization.
From a technological standpoint, the Cosmos project is highly promising, as the complexity of decentralized applications being developed is undoubtedly set to increase. There may come a time when the capabilities of older blockchain projects simply become insufficient.
Cosmos could potentially solve the crypto industry's growing problems, thanks to its openness and scalability potential. However, its closest competitor, Polkadot, also poses a significant challenge, making predictions difficult. Considering the advantages of the project and the ATOM cryptocurrency compared to competitors, it makes sense to mention the following facts:
- The Cosmos ecosystem has shown significant growth and continuous development since its launch.
- The Cosmos ecosystem community is active and engaged.
- The ATOM cryptocurrency has significantly increased in price: since the project's launch, its price has risen by more than 1500%.
The most famous projects created on the Cosmos base include Terra, Akash Network, and IRISnet. The ecosystem has also distinguished itself through partnerships with other blockchain projects, such as Binance and Kava.
Given the active community of the ecosystem and the announced future upgrades, improvements, interesting developments, and innovations, the network's future looks very promising. As the blockchain industry evolves and matures, the Cosmos ecosystem could become a leading player in this crypto space. Many experts believe the project is capable of offering a powerful alternative to other ecosystems.







 Back to articles
Back to articles

